New Approach For Hyperparameter Tuning
Design of Experiment based approach for Hyperparameter Tuning
I took the Design of Experiments class in the first semester of my MS Data Science Program at Georgia Tech. The course is very different than other Machine Learning classes that I took because of two main reasons –
The focus of the course was teaching applications of statistics (primarily ANOVA and Regression theory) in determining whether independent variables have significant effects on the response variable. This is a slightly different viewpoint than the one adopted during a modeling class (which focuses more on making predictions)
In modeling classes, we do not care about how we got the data, we just assume there is data and we have to create a model. This class actually focused on how to conduct the experiment, collect the data and then analyze the relationships between inputs and outputs.
The fundamental thing I learned in that course was – How to reduce the number of runs of an experiment so that we have enough data to comment on the relationship between independent and dependent variables.
Although there are many concepts that I learned during the class that is relevant to building ML models, in this post, I would like to expand upon the project that I did with one of my colleagues.
Getting straight to the point, our project proposed a new method to perform Hyperparameter Tuning. More details about the experiments that we performed can be found on this GitHub repo. There is a PDF file as well that explains each and every concept in great detail and that can also be found on the same repo. To summarise the methodology that we adopted look at the below pictures.
The motivation behind our appraoch can be summarized as -
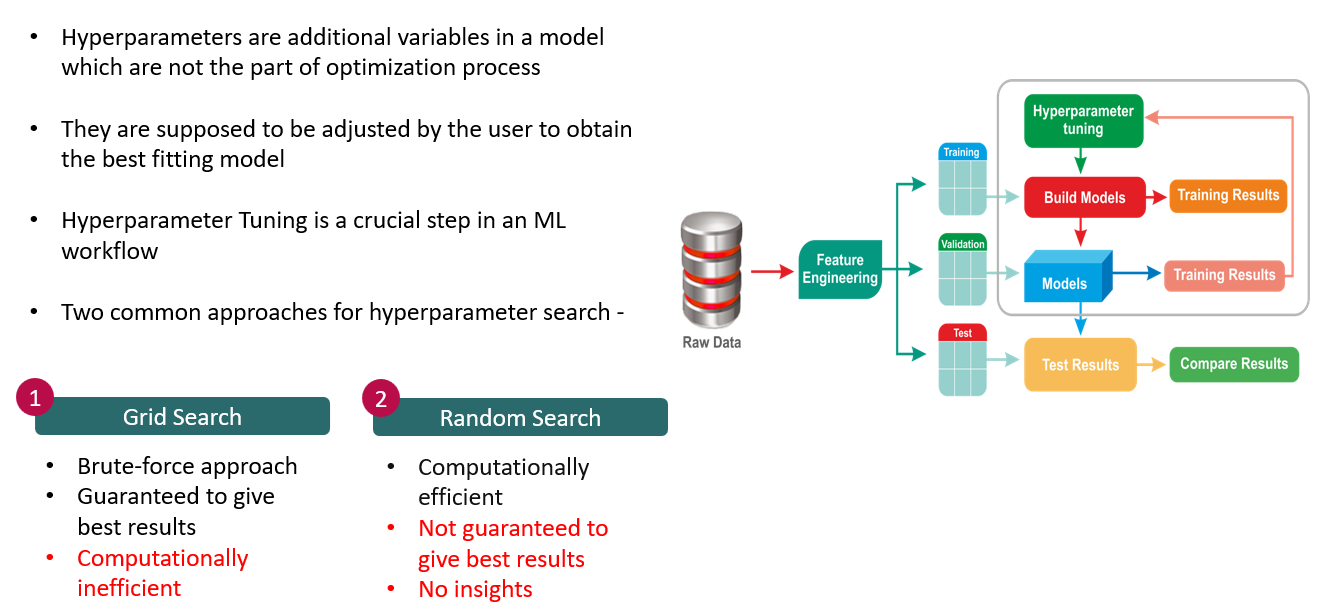
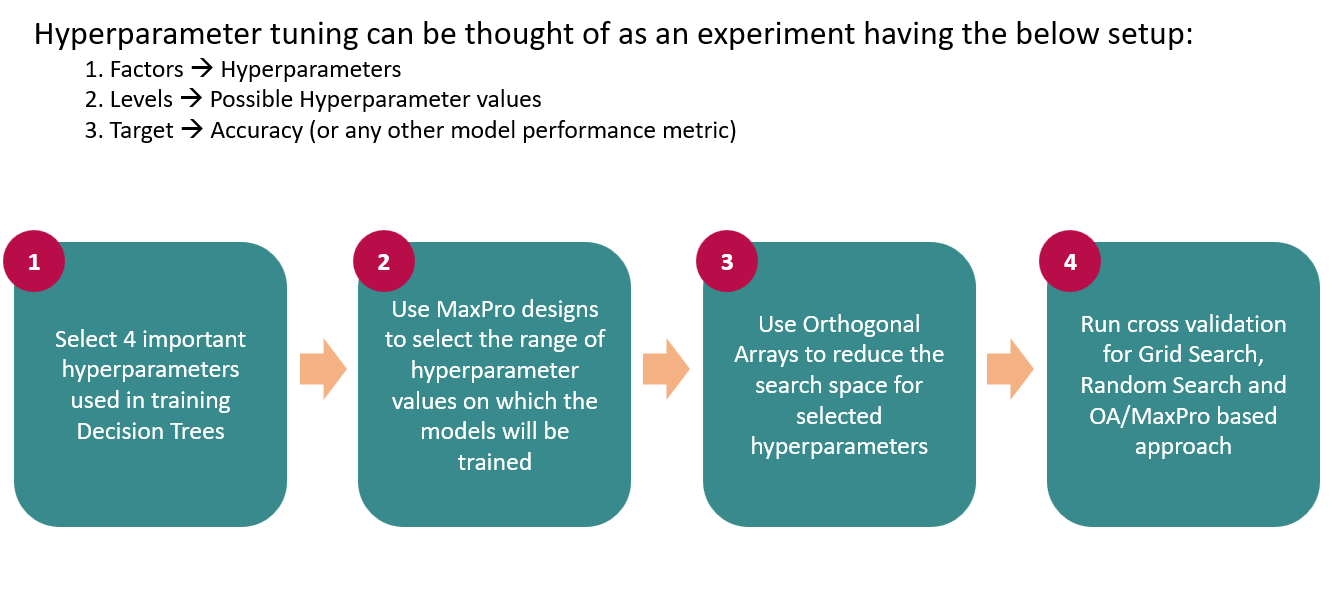
We followed a 4 step methodology to achieve the results -
After running the notebook in the repo, you’ll get the following results -

Finally, we can say that these are the 3 key benefits of this new approach -
-
Time Reduction – OA/MaxPro based hyperparameter tuning resulted in an improvement of 7.43 times as compared to Grid Search
-
Insights gained – Advantage over the Random Hyperparameter Search is the certainty of a good result and information gained about the effects of parameters on accuracy can help us make other modeling decisions in our project
-
Key Takeaway - Given computer experiments in the world of Machine Learning can be very expensive (single run of a model can take up to days even). Being able to reduce the search space and then gain actionable insight from the reduced space is a valuable addition to the Hyperparameter Search methodologies currently in play
